Fog Computing for 5G and IoT. As 5G and IoT continue to expand, fog computing is emerging as a critical technology for managing and processing massive amounts of data. Fog computing provides a middle ground between devices and centralized cloud data centers, enabling faster, more efficient processing and storage close to where data is generated. In this article, we’ll explore the role of fog computing in enhancing 5G and IoT capabilities, its key benefits, and how it’s changing the tech landscape.
What is Fog Computing?
Fog computing, or “fogging,” extends cloud capabilities to the edge of the network. It processes data close to the source rather than sending it to a centralized cloud, making it ideal for 5G and IoT applications that demand real-time responses. Fog Computing for 5G and IoT.
- Local Processing: Data is processed near the devices that generate it.
- Reduced Latency: Minimal delays since data doesn’t need to travel to and from distant servers.
- Enhanced Security: Data is kept closer to the source, reducing exposure to cyber threats.
Table of Contents
Why Fog Computing is Essential for 5G and IoT
1. Managing Data Deluge
- IoT devices constantly generate data, from smart thermostats to industrial sensors.
- Fog computing helps manage this flood of information by processing data locally, reducing the load on central networks. Fog Computing for 5G and IoT.
2. Real-Time Processing Needs
- Applications like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and industrial automation need immediate responses.
- Fog computing enables real-time processing, essential for latency-sensitive applications.
3. Bandwidth Optimization
- With fog computing, only necessary data is sent to the cloud, reducing bandwidth usage.
- This improves overall network efficiency and reduces costs.

Key Benefits of Fog Computing for 5G and IoT
Reduced Latency
- Processing data locally minimizes the time needed to send and retrieve data.
- Crucial for applications that require rapid responses, like connected health devices or smart traffic systems.
Enhanced Security and Privacy
- Sensitive data can be processed close to its source, reducing the risk of interception.
- Data can be stored locally on fog nodes, adding a layer of security. Fog Computing for 5G and IoT.
Increased Reliability
- Fog computing allows for continuous operation, even if the connection to the central cloud is disrupted.
- Essential for critical systems like industrial automation and autonomous vehicles.
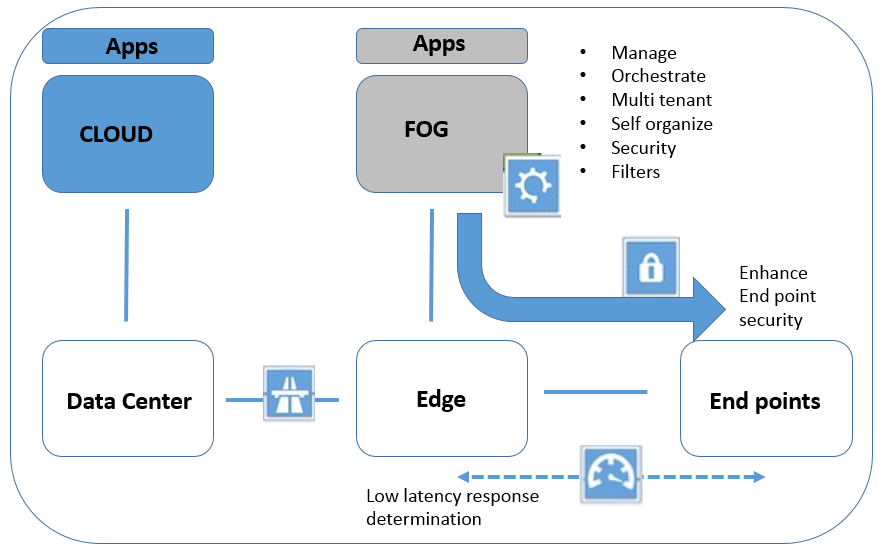
Fog Computing Architecture: How Does it Work?
- Edge Devices: Sensors, IoT devices, and other hardware collect and send data.
- Fog Nodes: Local processing units (e.g., routers, gateways) perform preliminary data processing.
- Central Cloud: Only relevant data is sent to the cloud for storage or further analysis.
By distributing processing across these layers, fog computing reduces congestion and increases processing speed.
Applications of Fog Computing in 5G and IoT
1. Smart Cities
- Traffic lights, public transit, and environmental sensors can function in real-time with fog computing.
- Allows for intelligent traffic management, reducing congestion and improving safety.
2. Healthcare
- Patient-monitoring devices rely on fast data processing to respond to changes in a patient’s condition.
- Fog computing ensures health data is processed locally, supporting immediate action in emergencies.
3. Industrial Automation
- Factories and production facilities use IoT devices to monitor and control equipment.
- Fog computing supports high-speed processing required for real-time adjustments and predictive maintenance.
4. Autonomous Vehicles
- Self-driving cars need rapid data processing to navigate and avoid hazards.
- Fog computing enables real-time decision-making by processing data closer to the vehicle.
Challenges and Limitations of Fog Computing
- Infrastructure Costs: Implementing fog nodes can be costly, especially for large-scale networks.
- Complexity in Management: Managing a decentralized system requires sophisticated orchestration and maintenance.
- Security Concerns: While fog computing can enhance security, it also introduces new challenges in protecting dispersed data.
Fog Computing vs. Edge Computing: What’s the Difference?
While fog and edge computing are often used interchangeably, they have distinct differences:
- Edge Computing: Processes data directly at the source, such as on an IoT device itself.
- Fog Computing: Extends processing to a network of local nodes, bridging the gap between edge devices and the cloud.
In essence, fog computing is an intermediary layer that supports more complex processing tasks, ideal for handling the vast data demands of 5G and IoT.
The Role of Fog Computing in Enhancing 5G Performance
- High-Speed Data Processing: 5G enables faster connections, and fog computing makes sure the data is processed at similar speeds.
- Better Network Congestion Management: By processing data locally, fog computing alleviates strain on 5G networks, allowing for smoother operations.
- Improved User Experience: Applications that rely on 5G can deliver more responsive, real-time experiences through fog computing.

Future of Fog Computing in IoT and 5G
As 5G networks and IoT devices become more widespread, fog computing will play an increasingly critical role:
- Growth in Autonomous Technologies: Autonomous vehicles, drones, and robotics will benefit from fog computing’s real-time data handling.
- Expansion of Smart Infrastructure: More cities and industries will adopt fog computing for efficient management of connected devices.
- Enhanced AI Applications: Fog computing will support AI at the edge, enabling quicker insights and decisions without relying solely on cloud processing.
Conclusion
Fog computing is revolutionizing how we manage and process data for 5G and IoT. By enabling localized data processing, fog computing addresses challenges like latency, bandwidth, and security, making it an essential technology for future IoT and 5G applications. As fog computing continues to evolve, it promises to unlock new possibilities in areas ranging from smart cities to autonomous vehicles.
FAQs
- How does fog computing differ from cloud computing?
- Fog computing processes data locally near the source, while cloud computing involves centralized data processing in remote servers.
- Why is fog computing important for 5G?
- Fog computing reduces latency and optimizes bandwidth, allowing 5G networks to handle data more efficiently and improve user experiences.
- Can fog computing work without the internet?
- Yes, fog computing can function without continuous cloud access, as it processes data locally, making it more reliable in disconnected environments.
- Is fog computing secure?
- Fog computing enhances security by keeping data closer to the source, but it still requires robust security measures to protect dispersed data.
- What industries benefit most from fog computing?
- Fog computing is valuable in industries like healthcare, automotive, industrial automation, and smart cities, where real-time data processing is crucial.


